Phloroglucinol derivatives are a major class of secondary metabolites. They are widely found in Myrtaceae, Moutonceae, Euphorbiaceae, Sporeaceae, Compositae, Rutaceae, Rosaceae, Cruciferae, Lauraceae, Crassulaceae, Cannabis and Fagaceae, etc. Section. Additionally, these compounds are also present in marine and microbial sources. Phloroglucinol compounds can be divided into monomers, dimers, trimers and higher phloroglucinol and phloroglucinol
Phloroglucinol is known for its broad-spectrum antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal, anthelmintic, and phytotoxic activities. 2,4-Diacetylphloroglucinol (2,4-DAPG), produced by plant-associated Pseudomonas, is particularly important in agriculture due to its antifungal activity.
Bangera and Thomashow proposed that PhlD condenses two malonyl-CoAs and one acetyl-CoA to form 2-monoacetylphloroglucinol, which is subsequently converted to 2,4-DAPG by PhlABC. 46 (2) However, Achkar et al. PhlD is proposed to condense three malonyl-CoAs to form phloroglucinol, which can also be converted to 2,4-DAPG by PhlABC (Scheme 7). 47 A study by Zha et al. 48 showed that acetoacetyl-CoA was not the preferred initiator for PhlD and that 2-monoacetylphloroglucinol was not produced from the reaction, suggesting that the hypothesis of Achkar et al. 47 is more likely.
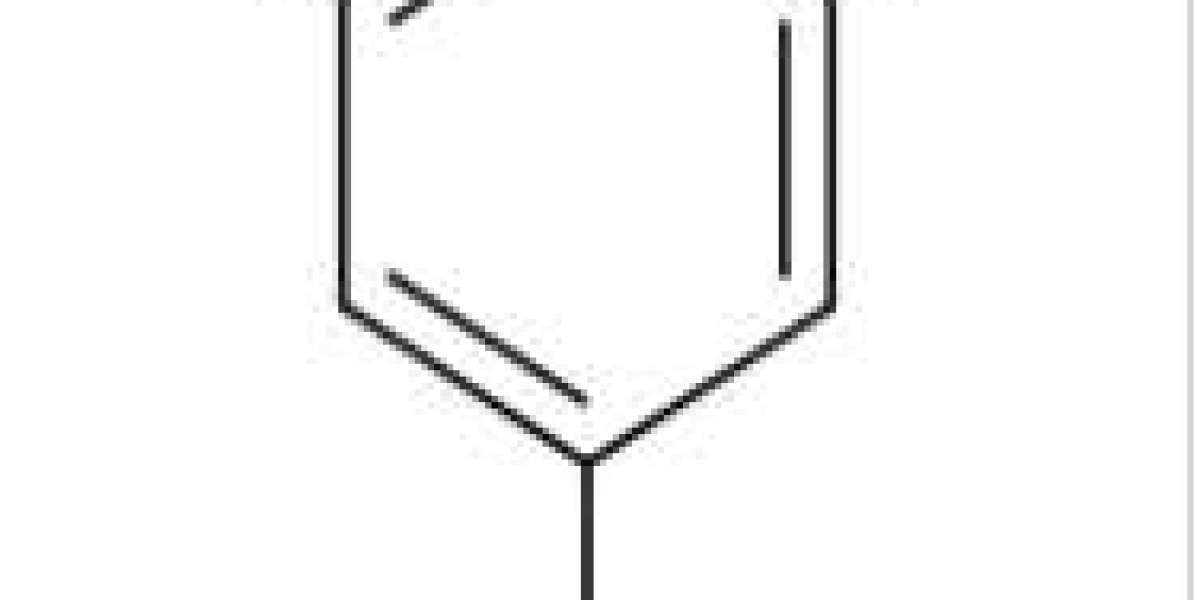
With respect to monomeric phloroglucinol, this group includes acryloylphloroglucinol, phloroglucinol-terpene adducts, phloroglucinol glycosides, halogenated phloroglucinol, prenylated phloroglucinol and cyclic polyketides. As for acylphloroglucinol, it is considered to be the largest class of compounds in phloroglucinol with natural properties. It contains more than 100 simple acylated phloroglucinols in addition to various types of derivatives. Considerable research has been done to synthesize these compounds with regard to their wide range of biological activities. Most congeners of phloroglucinol-terpene adducts have been isolated from different species of eucalyptus. According to the presence of chroman circles, they are divided into two groups: euglobals (with chroman adducts) and euglobals (without chroman adducts). Regarding phloroglucinol glycosides, there are more than 50 glycosides of phloroglucinol and its derivatives from natural sources. Phlorin, phloroglucinol β-d-glucoside (Fig. 3.9.2), is the simplest phloroglucinol glycoside, which has been isolated from cannabis, dogwood, and some citrus fruits. Halogenated phloroglucinols are mainly monohalogenated derivatives.