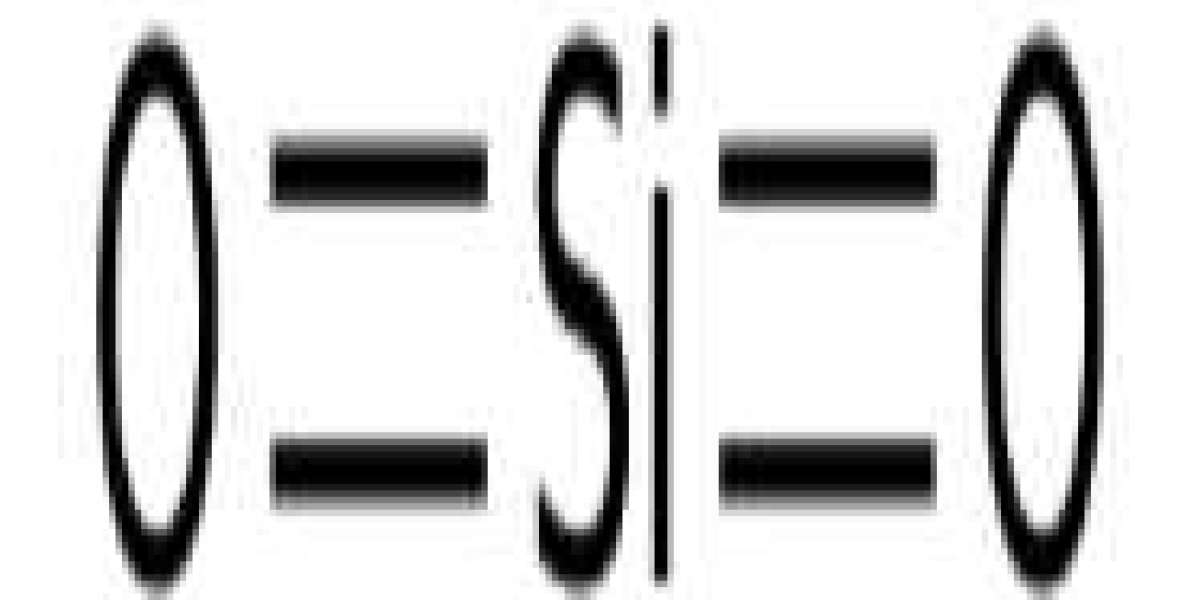Diatomaceous earth is a siliceous sedimentary rock composed primarily of the fossilized skeletal remains of diatoms, single-celled organisms related to algae. Diatomaceous earth has a porous structure, making it ideal for use as an insulation or filter material (its primary use)
Derived from the remains of microscopic fossilized seaweed, or freshwater algae, diatomaceous earth is a naturally occurring, versatile mineral used in a range of applications from cosmetics to filtration.
Diatomaceous earth is a sedimentary rock consisting of the fossilized skeletal remains of single-celled aquatic algae known as "diatoms." This unique form of silica has a delicate honeycomb structure filled with thousands of tiny pores ranging in diameter from a few micrometers to submicrometers. No other source of silica, whether mined or produced, exhibits this structure. Some diatomite deposits are brackish, but most come from freshwater sources.
When ground, this rich shape produces an extremely low density powder called "diatomaceous earth" (DE), which has excellent absorption properties and is prepared for use in filtration, agriculture, paints, plastics, cosmetics and pharmaceutical applications. Well respected - just to name a few.
In cosmetics, superabsorbent diatomaceous earth-based powders are ideal 100% natural ingredients in deodorants and antiperspirants. When used in a face mask, diatomaceous earth can significantly reduce the drying time of the clay.
In paints and coatings, diatomaceous earth is an excellent matting agent, providing sand and scrub resistance, breathability and crack resistance.
In plastic films, Imerys DE grades are effective antiblock additives that prevent films from sticking together during production, processing and end use.
Imerys also utilizes the special properties of diatomaceous earth for construction, pharmaceutical, plastics, rubber, polishing and oil spill applications.