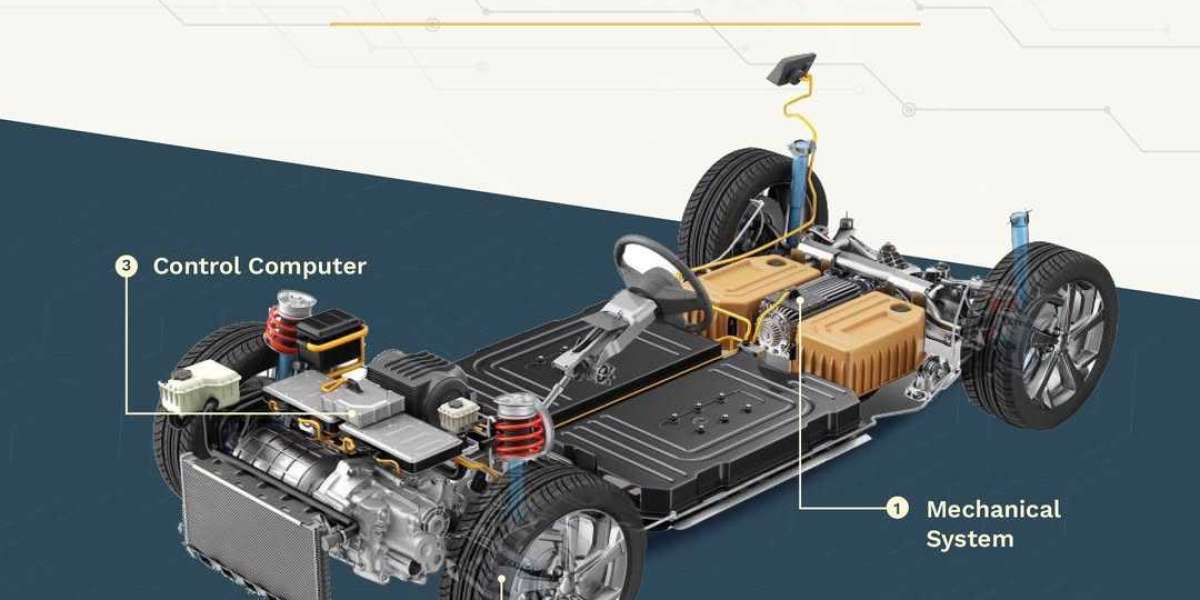
A mechatronic design engineer is a multidisciplinary expert who combines mechanical engineering, electronics, control systems, and software to design and develop innovative, intelligent systems. This role is pivotal in industries like automotive, robotics, aerospace, and consumer electronics, where the integration of diverse technologies drives progress. Mechatronic design engineers create solutions that are efficient, reliable, and adaptable, shaping the future of automation and smart technology. This article explores the role, skills, responsibilities, applications, challenges, and future of mechatronic design engineering.
What is a Mechatronic Design Engineer?
A mechatronic design engineer specializes in designing systems that integrate mechanical components with electronic controls and software. This involves developing devices like robots, automated machinery, and smart appliances that require precise coordination between hardware and software. Unlike traditional engineers focused on a single domain, mechatronic engineers adopt a holistic approach, ensuring all elements work seamlessly together. For example, designing a robotic arm involves crafting its mechanical structure, embedding sensors, programming control algorithms, and testing its performance.
Key Skills and Qualifications
Success in this field requires a blend of technical and soft skills:
- Technical Expertise: Proficiency in mechanical design (e.g., CAD software like SolidWorks), electronics (circuit design), and programming (C, C++, Python).
- Control Systems Knowledge: Understanding feedback loops, PID controllers, and real-time systems.
- Problem-Solving: Ability to troubleshoot complex, interdisciplinary issues.
- Collaboration: Working with cross-functional teams, including software developers and manufacturing experts.
- Education: A degree in mechatronics, mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, or a related field, often supplemented by certifications or advanced training.
Responsibilities of a Mechatronic Design Engineer
The role encompasses a wide range of tasks:
- System Design: Creating conceptual designs that integrate mechanical, electronic, and software components.
- Prototyping: Building and testing prototypes to validate functionality and performance.
- Programming: Developing firmware or software to control embedded systems.
- Testing and Validation: Conducting simulations and real-world tests to ensure reliability and safety.
- Optimization: Refining designs to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance durability.
- Project Management: Overseeing timelines, budgets, and team coordination from concept to production.
Applications of Mechatronic Design Engineering
Mechatronic design engineers impact numerous sectors:
- Automotive: Designing advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), electric vehicle powertrains, and autonomous driving technologies.
- Robotics: Developing industrial robots, humanoid robots, and collaborative robots (cobots) for manufacturing and healthcare.
- Aerospace: Engineering flight control systems, drones, and satellite mechanisms with precision.
- Consumer Electronics: Innovating smart home devices, wearable tech, and gaming consoles.
- Industrial Automation: Creating automated assembly lines, CNC machines, and process control systems.
Challenges Faced by Mechatronic Design Engineers
The multidisciplinary nature of the role presents unique challenges:
- Integration Complexity: Aligning mechanical, electrical, and software components requires meticulous coordination.
- Resource Constraints: Designing within limited budgets, space, and power requirements.
- Rapid Technological Change: Keeping pace with advancements in sensors, processors, and software.
- Testing Rigor: Ensuring systems perform reliably under diverse, often harsh conditions.
- Safety Concerns: Meeting stringent safety standards, especially in automotive and medical applications.
Tools and Technologies
Mechatronic design engineers rely on advanced tools:
- CAD Software: For mechanical design (e.g., AutoCAD, SolidWorks).
- Simulation Tools: MATLAB/Simulink for modeling and testing control systems.
- Embedded Systems Platforms: Arduino, Raspberry Pi, and microcontrollers for prototyping.
- Programming Environments: IDEs like Keil or Eclipse for coding and debugging.
- Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL): For real-time validation of integrated systems.
Future Trends in Mechatronic Design Engineering
The field is evolving with technological advancements:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Integrating AI for adaptive control and predictive maintenance in mechatronic systems.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Connecting devices for smart, networked solutions like smart factories.
- Additive Manufacturing: Using 3D printing to create complex mechanical components rapidly.
- Miniaturization: Developing smaller, more efficient systems for wearables and medical devices.
- Sustainability: Focusing on energy-efficient designs to support green technology initiatives.
The rise of Industry 4.0 and autonomous systems further amplifies the demand for mechatronic expertise, with engineers playing a key role in the fourth industrial revolution.
Career Prospects and Growth
Mechatronic design engineers enjoy a dynamic career path with opportunities for growth. Entry-level roles may involve assisting in design or testing, while experienced engineers can advance to lead design positions, project management, or research and development. The global push for automation and smart technology ensures a robust job market, with competitive salaries and the potential for international collaboration.
Conclusion
Mechatronic design engineers are at the forefront of technological innovation, blending mechanical ingenuity with electronic and software expertise. Their work powers the devices and systems that define modern life, from self-driving cars to robotic surgery tools. Despite challenges, the field’s future is bright, driven by trends like AI, IoT, and sustainability. As industries continue to evolve, mechatronic design engineers will remain essential in creating smarter, more efficient, and interconnected solutions.