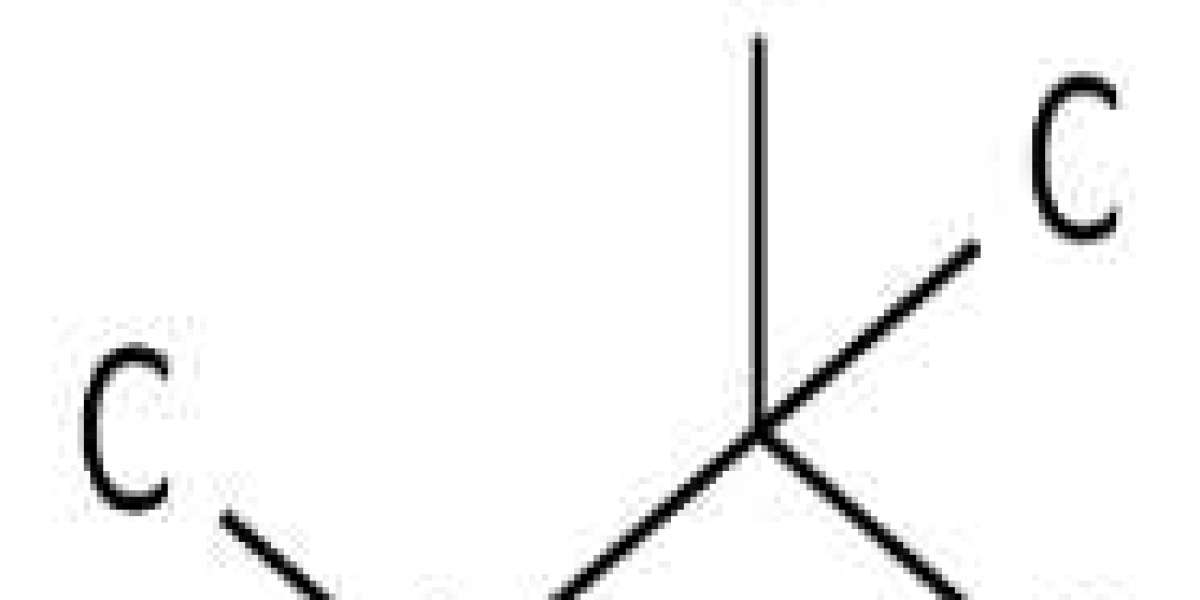
Methyl tert-butyl ether may be one of the first chemicals to show up in drinking water wells in the region when underground storage tanks leak. Most people can smell Methyl tert-butyl ether in contaminated water at concentrations as low as 100 parts per billion (ppb).
Methyl tert-butyl ether is used as a gasoline additive. Exposure may occur by breathing polluted air
Emitting vehicle exhaust or gasoline fumes when refueling your vehicle. Respiratory irritation, dizziness and
Some motorists and occupational exposure workers reported disorientation. Acute (short-term) exposure to Methyl tert-butyl ether has also occurred in humans during its use as a medical
Treatment for dissolving cholesterol gallstones. Chronic (long-term) inhalation exposure to methyl-tert-butyl
Ether can cause central nervous system (CNS) effects, respiratory irritation, hepatic and renal effects,
and reduce the weight gain of the animals. Developmental effects have been reported in rats and mice
Exposure by inhalation. EPA does not classify potential Methyl tert-butyl ether
Carcinogenicity.
Almost all Methyl tert-butyl ether produced in the U.S. is used as an additive in unleaded gasoline
to boost octane and reduce carbon monoxide emissions.
It has been used in the past to produce isobutene.