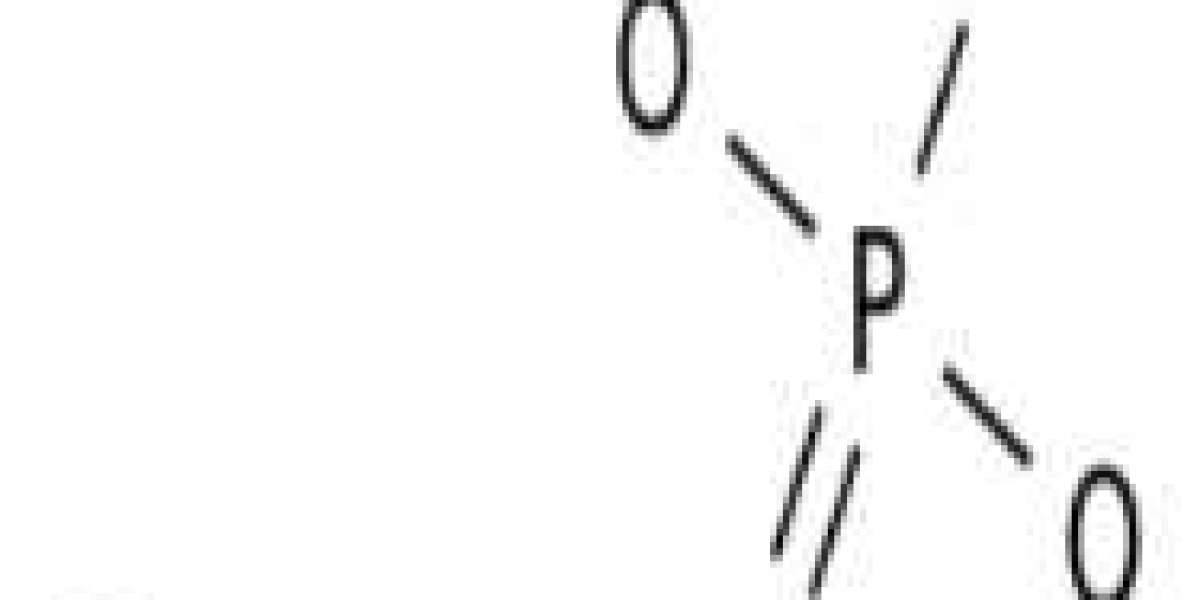
What is magnesium phosphate?
Magnesium phosphate (m3 (PO4)2) is an important mineral found in bones, seeds of many plants, and many minerals. It is used as a supplemental source of dietary magnesium. Tribasic magnesium phosphate can be prepared by the interaction of magnesium chloride or magnesium sulfate with phosphate. The solution can be easily prepared by mixing some salt with CO2-free water for several hours.
Magnesium phosphate is a salt that when treated with water forms phosphoric acid and magnesium hydroxide. The chemical equation is given below.
What uses does magnesium phosphate have?
Magnesium phosphate is widely used in medicine to support muscle relaxation. The compound is also used to prevent muscle cramps. Magnesium phosphate is also used to prevent vitamin E deficiency.
What happens when magnesium phosphate mixes with water?
When treated with water, magnesium phosphate participates in the formation of magnesium hydroxide and phosphoric acid as products.
How does magnesium phosphate react with hydrochloric acid?
Magnesium phosphate reacts with hydrochloric acid to form magnesium chloride and phosphoric acid.
Magnesium phosphate is an ionic compound composed of magnesium ion (Mg2+) and phosphate anion (PO43-). This is a salt with a hydrated crystalline structure. During hydration, water of crystal is present in the crystal structure of magnesium phosphate. It also exists in an amorphous form. The molecular formula of magnesium phosphate is Mg3(PO4)2 and the molecular weight of magnesium phosphate is 262.855 g/mol. This salt occurs in nature as mono-magnesium phosphate hydrate, dimagnesium phosphate, or trimagnesium phosphate hydrate. It looks like white crystalline powder. The concentration at 298K was 2.195 g/mL. It has a melting point of 1457K.
The structure of magnesium phosphate
In the most common magnesium phosphate, three divalent magnesium cations and two phosphate anions are attracted by electrostatic attraction, resulting in the electricity price structure of magnesium phosphate. Water of crystal molecules may also attach to their crystals.