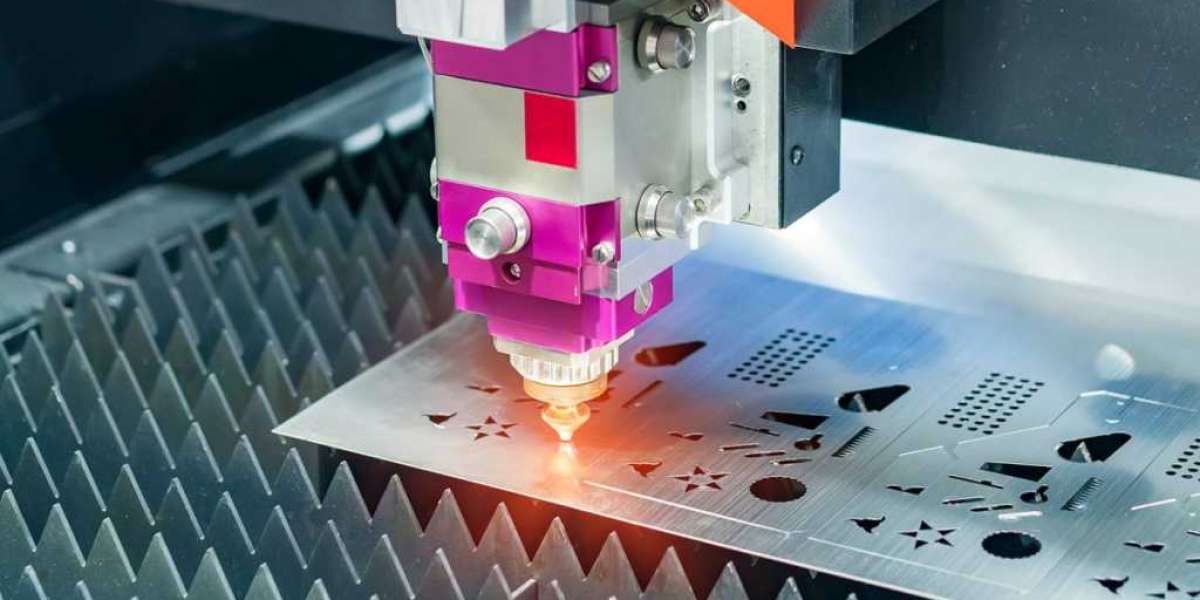
The laser machine design plays a pivotal role in determining its precision and efficiency, especially in industrial applications. Laser technology has made remarkable strides in the manufacturing sector, where it is used for tasks ranging from cutting and engraving to welding and marking. The ability to achieve high precision and operational efficiency depends heavily on how the laser machine is designed, including aspects such as its mechanical structure, optics, laser source, control systems, and cooling mechanisms.
The Role of Mechanical Design in Laser Machines
The mechanical design of a laser machine refers to the framework that houses all the essential components, such as the laser source, beam delivery system, motion system, and workpiece handling. The structural integrity of the design is crucial for maintaining the accuracy and stability of the system during operation.
For instance, any minor movement or vibration in the frame can lead to misalignment of the laser beam or the material being worked on, which ultimately compromises the precision of the cutting, engraving, or welding process. A well-engineered design ensures that the machine remains rigid and stable, even under high-speed or heavy-duty operations.
Components like linear rails, servo motors, and ball screws in the motion system are also part of the mechanical design and significantly affect the overall performance. These parts determine the precision with which the laser machine can move its head, which is essential for intricate designs or cuts.
The rigidity of the machine’s frame must match the expected workload. For example, a laser machine designed to cut thick metal sheets requires a much more robust structure than one designed for fine engraving on small parts. The mechanical design is not only responsible for providing the necessary support but also for minimizing distortions or shifts during high-speed movements.
Importance of Optics in Laser Machine Design
The optical design in a laser machine refers to how the laser beam is focused and directed onto the material being processed. The optics system includes lenses, mirrors, and beam delivery systems, and it is one of the most critical elements of laser machine design when it comes to ensuring precision.
The lens system, in particular, plays a vital role in focusing the laser beam down to a small, accurate spot on the material. The design of these lenses and mirrors directly impacts the focal length and beam quality, which are essential for achieving high precision. For instance, a lens with a shorter focal length can produce a more concentrated beam, which is useful for cutting or engraving fine details.
The beam delivery system must be designed to efficiently transport the laser from the source to the workpiece without significant energy loss or distortion. Any imperfection in the optics can result in a scattered beam, which not only affects the cut quality but can also reduce the efficiency of the laser machine.
In addition to the basic components of the optics system, the overall design must take into account factors such as the wavelength of the laser, which influences the interaction between the laser and the material being worked on. Certain materials are more responsive to specific wavelengths, and the laser machine’s optical design must be compatible with the material being processed for optimal results.
Laser Source and Power in Design
Another integral part of the laser machine’s design is the laser source itself. Different types of lasers—such as CO2 lasers, fiber lasers, and solid-state lasers—have unique characteristics, and the choice of laser source is dictated by the specific application. Each laser source type has its own design requirements for power output, wavelength, and efficiency.
The laser source design directly impacts the cutting speed and depth of penetration in materials. For example, fiber lasers are known for their ability to cut through metals at a high rate of speed due to their high power density. The machine must be designed to handle the heat generated by these sources and to focus the laser with extreme precision.
A well-designed laser machine ensures that the power output of the laser is stable and consistent throughout the operation. This consistency is crucial for maintaining the precision of the cut and ensuring that the material is processed evenly across the entire surface. Fluctuations in power can lead to uneven cuts, burns, or incomplete processing, all of which can compromise the quality of the work.
Moreover, the design of the power supply system is also an important consideration. The power system must be capable of delivering the necessary power for the laser source, while also being energy efficient. This is essential in industrial applications where laser machines are expected to run for extended periods of time.
Control Systems and User Interface Design
Modern laser machines rely heavily on sophisticated control systems to drive the machine’s movement, monitor its operation, and interact with the operator. The design of the control system is vital in determining the machine's overall precision and efficiency.
The control system interprets the operator’s inputs (usually in the form of CAD/CAM files) and translates them into machine movements, adjusting parameters such as the laser power, speed, and focus. It also synchronizes the motion of the machine with the laser output to ensure that the correct amount of energy is applied to the material at the right time.
The software interface is another crucial design element. A user-friendly interface allows operators to easily program the machine and monitor its performance. Advanced systems often incorporate automated feedback loops, which continuously adjust the laser parameters in real-time based on the feedback from sensors. This ability to make real-time adjustments helps to ensure that the laser machine maintains a high level of precision throughout the operation.
The software also governs the machine’s safety features, ensuring that the laser is operating within the specified parameters and preventing malfunctions or unsafe conditions. For example, if the laser encounters an unexpected resistance from the material, the control system may automatically adjust the laser’s power output or stop the process altogether to avoid damaging the machine or the material.
Cooling Systems and Thermal Management
Laser machines, especially those with high-power lasers, generate significant amounts of heat during operation. This heat can affect the performance of the laser and other components, making the design of an effective cooling system essential to maintaining precision and efficiency.
Laser machines typically use either water or air cooling systems to manage heat dissipation. The design of the cooling system ensures that the laser source remains at a consistent operating temperature, preventing overheating that could lead to a loss of performance or even permanent damage to components.
The cooling system also extends to the optics and motion systems. Lenses, mirrors, and other optical components can be sensitive to temperature fluctuations, and keeping these parts cool ensures that the laser beam remains stable and focused.
Without an efficient cooling system, the laser machine may experience thermal distortion, which can degrade the quality of the work and reduce the efficiency of the operation. Furthermore, excessive heat buildup could cause wear and tear on the machine, leading to increased maintenance costs and downtime.
Material Handling and Automation in Laser Machines
The design of a laser machine’s material handling system is another key factor in determining its efficiency. For industrial applications that involve high volumes of material processing, automation in the material handling system can greatly improve productivity. Automated loading and unloading systems can feed materials into the laser machine without requiring manual intervention, reducing the time required for each operation and minimizing human error.
The integration of automation systems into the laser machine’s design ensures that the process can run continuously, without interruption, for extended periods. This is particularly valuable in high-throughput environments where efficiency is critical to meeting production targets.
Additionally, the material handling system must be designed to accommodate various sizes and types of materials. The flexibility of the machine’s design to handle different workpieces can significantly improve its overall efficiency and adaptability to various tasks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the design of a laser machine is integral to its precision and efficiency in industrial applications. From the mechanical structure and optics system to the control systems, laser source, cooling mechanisms, and material handling systems, every design element plays a role in ensuring that the machine performs optimally. The complexity of modern laser machines requires careful consideration of these factors to achieve the best possible results, making design a fundamental aspect of laser technology. By optimizing the various components and ensuring that they work in harmony, manufacturers can ensure that their laser machines deliver the highest levels of precision, efficiency, and reliability in a wide range of industrial applications.