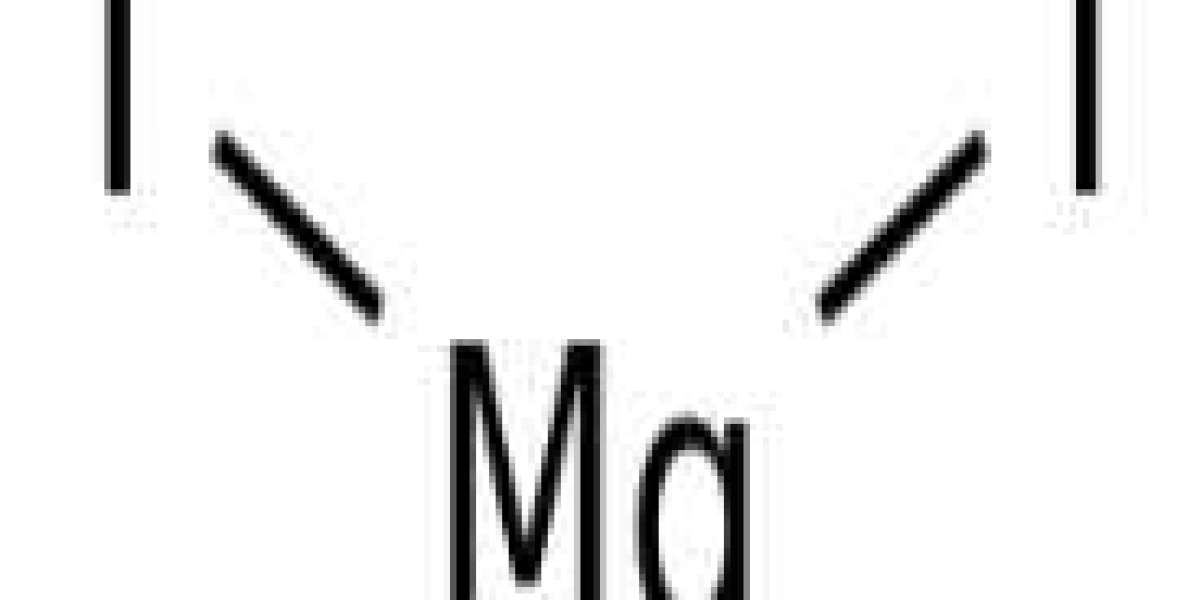
3-Pentanone (also known as diethylketone) is a simple, symmetrical dialkylketone. It is a colorless liquid ketone with an acetone-like odor. Soluble in about 25 parts of water, but miscible with organic solvents.
It is mainly used as a solvent for paints and a precursor of vitamin E.
3-Pentanone is produced by the keto-decarboxylation of propionic acid using a metal oxide catalyst
In the laboratory, the reaction can be performed in a tube furnace.
It can also be prepared by combining ethylene, CO, and H2. [3] Water can be used as a hydrogen source when the reaction is catalyzed by dicobalt octacarbonyl. The proposed intermediate is the ethylene-propionyl species [CH3C(O)Co(CO)3(ethylene)], which undergoes migratory insertion to form [CH3COCH2CH2Co(CO)3]. The required hydrogen comes from the water shift reaction. For details, see [5] If the water shift reaction does not work, this reaction provides polymers containing alternating carbon monoxide and ethylene units. Such aliphatic polyketones are more conventionally prepared using palladium catalysts.
3-Pentanone has a TLV of 200 ppm (705 mg/m3). [3] 3-Pentanone is dangerous if it comes in contact with the skin or eyes, causing redness, tearing and itching of the skin and eyes. The chemical can also cause damage to the nervous system or organs if ingested. Although considered stable, 3-pentanone is extremely flammable if exposed to a flame, spark, or other heat source. For safety, it should be stored in a flammable materials cabinet away from heat or ignition, preferably in a cool, well-ventilated area. [7]
3-pentanone is a natural product that occurs in Cichorium endivia, Zingiber mioga, and other organisms for which data are available.