Pulmonary Hypertension (PH) is a serious and progressive medical condition that affects the arteries in the lungs and the right side of the heart. Often misunderstood or misdiagnosed in its early stages, PH can have a significant impact on daily life and long-term health. This article provides a comprehensive overview of what pulmonary hypertension is, its causes, symptoms, how it’s diagnosed, and current treatment approaches.
What Is Pulmonary Hypertension?
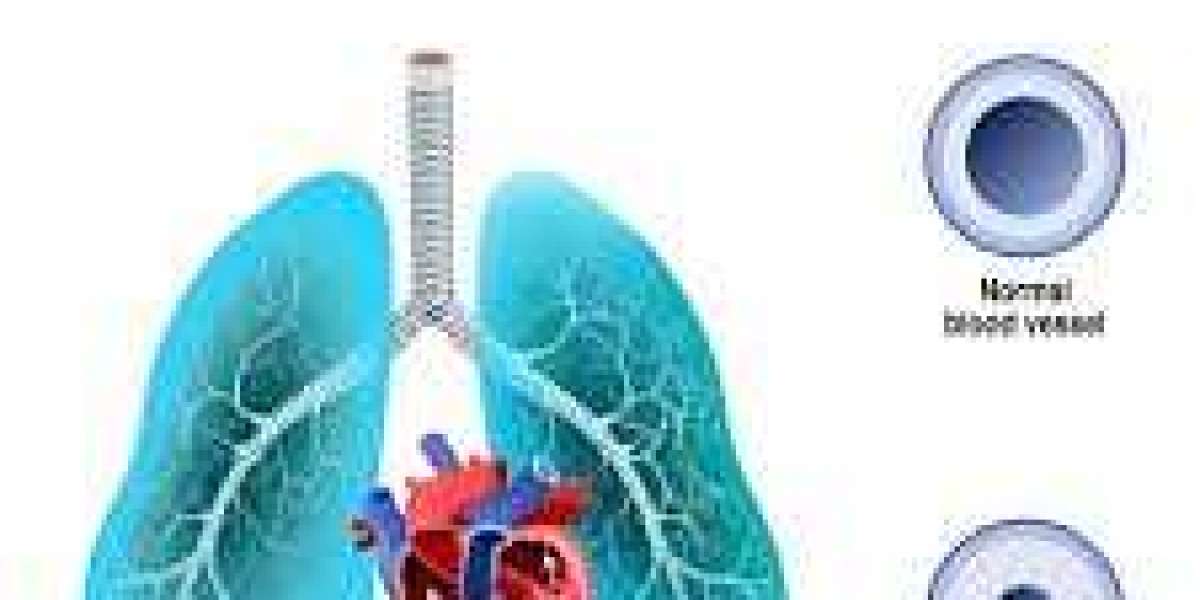
Pulmonary Hypertension occurs when the blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries—the vessels that carry blood from the heart to the lungs—rises to unhealthy levels. Unlike regular hypertension (high blood pressure), PH affects only the lungs and heart’s right side, leading to complications such as right heart failure if left untreated.
The pressure build-up occurs because the blood vessels in the lungs become narrowed, blocked, or damaged. As a result, the heart must work harder to pump blood, putting extra strain on the heart muscles.
Types of Pulmonary Hypertension
There are five major types of PH, categorized by their underlying causes:
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) – Caused by narrowing of the small arteries in the lungs.
PH Due to Left Heart Disease – Often caused by conditions such as heart failure or valve disease.
PH Due to Lung Disease or Hypoxia – Linked to COPD, interstitial lung disease, or sleep apnea.
Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension (CTEPH) – Results from blood clots in the lungs.
PH With Unclear or Multifactorial Causes – Includes conditions like sarcoidosis or sickle cell disease.
Common Symptoms of PH
Pulmonary Hypertension symptoms often develop slowly, making it easy to confuse with other conditions. Some of the most common include:
Shortness of breath during everyday activities
Fatigue and weakness
Chest pain or pressure
Swelling in the ankles, legs, or abdomen
Light-headedness or fainting
Rapid heartbeat (palpitations)
As PH progresses, these symptoms become more severe and interfere with basic activities.
What Causes Pulmonary Hypertension?
The causes depend on the type of PH but may include:
Genetic predisposition
Autoimmune diseases like lupus or scleroderma
Chronic lung conditions
Heart valve disorders
Long-term high blood pressure
Blood clots in the lungs
In many cases, no clear cause is identified, especially in idiopathic PAH.
Diagnosing Pulmonary Hypertension
Diagnosis typically involves multiple tests to confirm the presence and severity of PH:
Echocardiogram – Estimates pressure in the pulmonary arteries
Right Heart Catheterization – Measures actual pressure and confirms diagnosis
Pulmonary Function Tests – Assess lung health
CT Scans or MRI – Examine lung and heart structure
Blood Tests – Help rule out other diseases
Prompt diagnosis can slow progression and improve outcomes significantly.
Treatment Options for PH
While there is no cure for pulmonary hypertension, a range of treatments can manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
1. Medications
Vasodilators – Relax blood vessels in the lungs
Endothelin Receptor Antagonists – Block substances that narrow vessels
Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors – Help the heart and lungs work more efficiently
Anticoagulants – Prevent blood clots
Diuretics – Reduce fluid buildup
Patients often discuss options and trusted brands with healthcare professionals, including options like fildena professional (as prescribed), though it is not a primary treatment for PH.
2. Lifestyle Changes
Avoid smoking and secondhand smoke
Stay physically active with light exercises
Maintain a healthy diet and weight
Avoid high altitudes or air travel without oxygen support
Monitor oxygen levels regularly
Living with Pulmonary Hypertension
Managing PH requires a long-term commitment to treatment and lifestyle adjustments. Emotional support, regular follow-ups, and a strong healthcare team are crucial for stability. Many patients live fulfilling lives with proper management, though adjustments are necessary.
Support groups and online communities offer encouragement and shared experiences that can make the journey less isolating.
Conclusion
Understanding pulmonary hypertension is the first step toward managing its challenges. While it's a complex and often misunderstood condition, advancements in treatment and awareness have made it increasingly manageable. If you or a loved one experiences symptoms, seek medical advice early—it could make a life-saving difference.