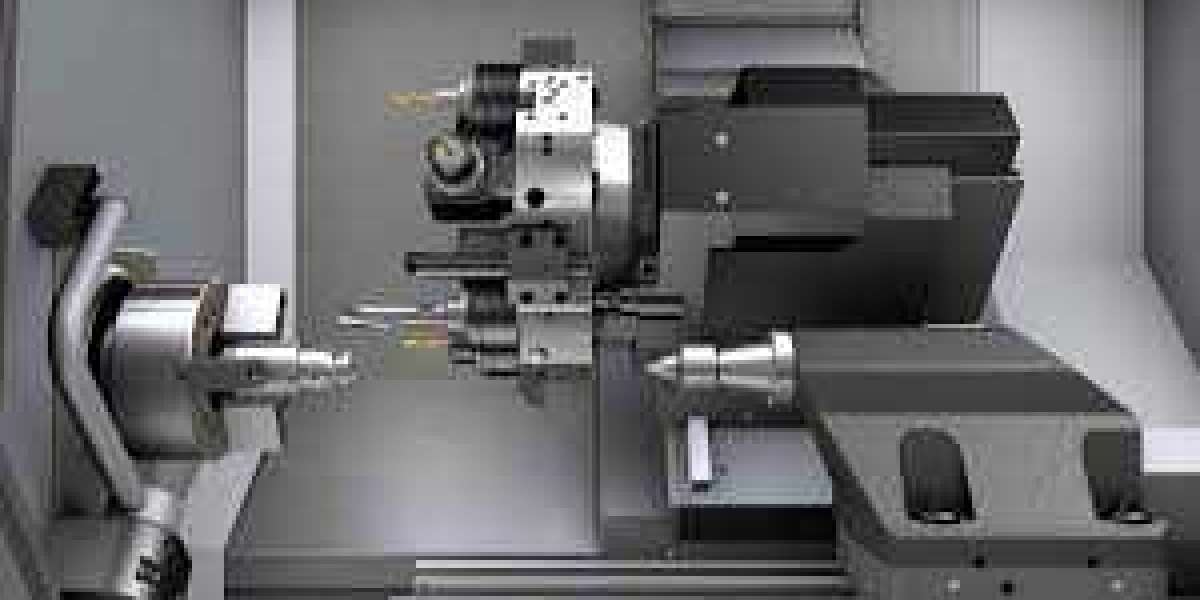
In the world of manufacturing, precision is key. Whether it's aerospace, automotive, or electronics, the need for accuracy in the production process cannot be overstated. This is where CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines come into play. CNC machines are at the heart of modern manufacturing, offering high levels of precision and automation. The various parts of CNC machines work together to ensure that the final product meets exact specifications. In this article, we will explore how the different components of CNC machines interact to provide superior accuracy and efficiency in the manufacturing process.
The Basics of CNC Machines: An Overview of Their Parts
CNC machines are automated tools that are controlled by a computer, allowing for precise cutting, shaping, and finishing of materials. At the core of CNC technology are several key parts of CNC machines, each playing a unique role in the machine's operation. The main parts include the controller, spindle, tool turret, linear guides, and the workpiece holding system. Each of these components works in harmony to execute the desired task with accuracy and speed.
The controller, often referred to as the brain of the CNC machine, processes the input from the operator and translates it into commands that the machine can follow. This is paired with the spindle, which holds and rotates the cutting tool at high speeds. The tool turret or tool changer stores various tools used in the process, while the linear guides and motors ensure smooth, precise movement of the machine along the X, Y, and Z axes. The workpiece is held firmly in place by a fixture or chuck, allowing the cutting tools to operate without interference.
The Role of the Spindle in CNC Machines
One of the most important parts of CNC machines is the spindle, which drives the cutting tool. The spindle is powered by a motor and is responsible for rotating the tool at high speeds. It is critical in determining the machine’s ability to perform fine and intricate cuts with precision. The speed at which the spindle rotates is often adjustable, allowing operators to tailor the machine's operation to the material being worked on. For example, harder materials require slower spindle speeds, while softer materials can be processed more efficiently with higher speeds.
The spindle must be designed to handle the forces involved in cutting or shaping materials. High-quality spindles are constructed with tight tolerances to ensure stability and precision. They often incorporate cooling systems to prevent overheating, which can negatively affect the quality of the machining process. A precise and stable spindle ensures that the cutting tool remains firmly in place, producing consistent and accurate results for every part produced.
The Importance of Linear Guides and Motors
Another vital component in parts of CNC machines is the system of linear guides and motors. The linear guides are mechanical components that allow the movement of the CNC machine along the X, Y, and Z axes. These guides ensure smooth, straight-line motion, allowing the cutting tool to follow the exact path dictated by the computer’s instructions. Any deviation in the motion could lead to inaccuracies in the final product, so the quality of these guides directly affects the precision of the CNC machine.
The motors that drive the linear guides are typically stepper motors or servo motors, which provide the necessary force to move the machine components. These motors are highly sophisticated and can be controlled with great precision to ensure that the movement of the machine is both accurate and repeatable. High-performance motors are designed to handle the heavy loads and dynamic forces involved in machining operations, further enhancing the machine's ability to produce parts with tight tolerances.
The Role of the Workpiece Holding System
For CNC machines to work accurately, the workpiece must be securely held in place during the machining process. This is where the workpiece holding system, such as a vice, chuck, or fixture, comes into play. These devices ensure that the material being worked on remains stationary, preventing any shifting or movement that could compromise the precision of the cut. A workpiece that moves during machining can cause misalignment, resulting in defects and dimensional inaccuracies.
The workpiece holding system is also critical in ensuring that the cutting tools can access the correct areas of the material. In CNC machines, the setup of the workpiece is often automated and controlled by the machine’s controller. For example, a fixture can be designed to hold the workpiece at a specific angle, making it easier for the cutting tool to reach the desired part of the material. With proper workpiece management, CNC machines can perform complex operations, such as drilling, milling, and turning, with high accuracy.
Tool Changes and Automation: The Efficiency of CNC Machines
One of the key advantages of CNC machines is their ability to perform automated tool changes. The parts of CNC machines that manage tool changes, such as the tool turret or tool changer, make it possible for the machine to switch between different tools without manual intervention. This automation allows CNC machines to perform multiple tasks, such as drilling, milling, or tapping, within the same program. The tool turret or changer can store a variety of tools, allowing the machine to automatically select the right one based on the task at hand.
This system of automated tool changes not only increases efficiency but also reduces the chances of human error. By eliminating the need for manual tool changes, CNC machines can operate continuously and produce parts with a high degree of consistency. Additionally, the tool changer ensures that each tool is used optimally, further enhancing the machine's precision. Automation in CNC machines also reduces downtime and allows for faster production cycles, making them invaluable in high-volume manufacturing environments.
Conclusion
The parts of CNC machines work together in a highly coordinated manner to achieve the precision and efficiency required in modern manufacturing. From the controller that interprets the operator’s commands to the spindle that drives the cutting tool, each component plays an essential role in ensuring accurate and high-quality results. The movement of the machine is governed by the linear guides and motors, while the workpiece holding system guarantees that the material remains stable throughout the process.
Furthermore, the ability of CNC machines to automate tasks like tool changes significantly increases their versatility and productivity. This combination of automation, precision engineering, and powerful components makes CNC machines a cornerstone of modern manufacturing. Understanding how these parts function together helps in appreciating the complexity and capability of CNC technology, as well as its importance in producing precision parts that meet the highest industry standards.