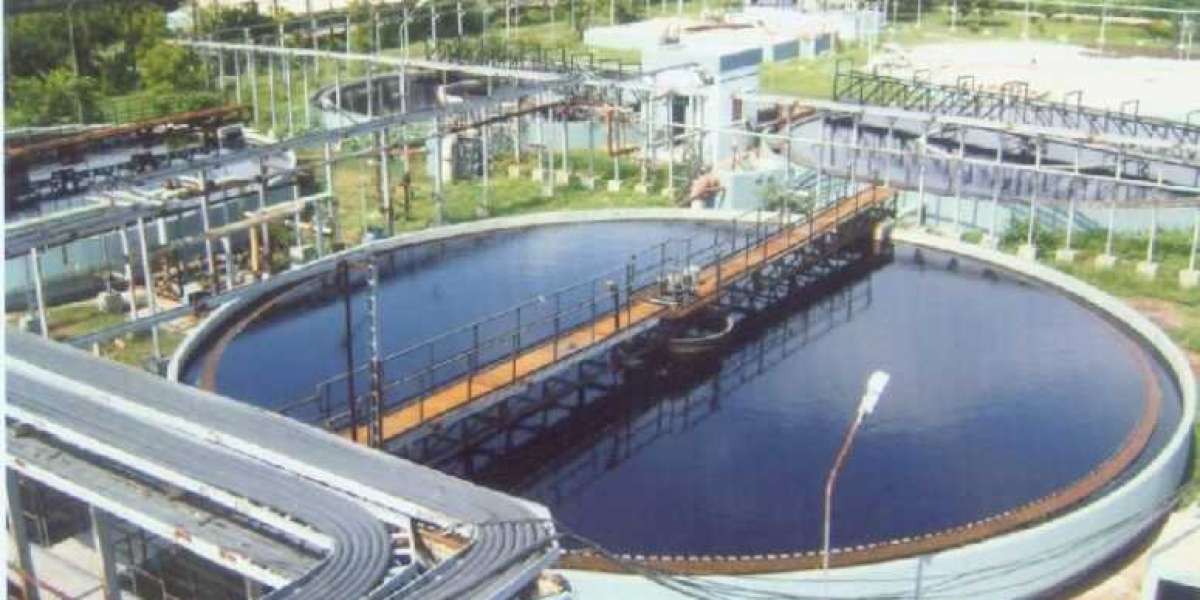
With sustainability becoming a cornerstone of modern architecture and urban planning, green buildings are more than just a trend—they’re a necessity. Green building compliance involves meeting environmental standards set by certification bodies like LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design), IGBC (Indian Green Building Council), or GRIHA (Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment). One critical aspect of this compliance is the effective management of wastewater, which underscores the vital role of Sewage Treatment Plants (STPs).
Why Wastewater Management Matters in Green Buildings
Green buildings aim to minimize their ecological footprint through efficient resource use, and water is a top priority. As water scarcity looms large, treating and reusing wastewater becomes essential. STPs enable buildings to reduce freshwater consumption by recycling water for non-potable uses such as flushing, landscaping, and cooling towers.
STPs and Green Certification Requirements
Most green building rating systems include wastewater treatment as a key parameter. For example:
IGBC and LEED recommend or mandate on-site STPs in residential, commercial, and institutional buildings.
GRIHA awards points for treating 100% of wastewater and reusing at least 50% within the premises.
By integrating an STP, developers can achieve higher compliance scores, improve marketability, and contribute to sustainable development goals (SDGs).
Benefits of STPs in Green Buildings
Reduces water bills by promoting internal reuse.
Prevents pollution by treating sewage before discharge.
Contributes to rainwater harvesting and water-positive practices.
Improves project sustainability rating and resale value.
Key Considerations for Installing an STP
Ensure the plant capacity matches the building’s occupancy.
Opt for low-maintenance, energy-efficient systems like MBBR or SBR.
Plan for sludge management and proper odor control.
Conclusion
To achieve green building compliance, installing a sewage treatment plant is not just a box to check—it's a forward-thinking investment. It demonstrates a commitment to sustainability, resource conservation, and responsible development, all while meeting regulatory standards and enhancing the building's long-term value.