Colorless, translucent lumps or hard, white, odorless crystals.
Boron oxide is colorless translucent glass block or white hard odorless crystal. Melting point 450°C; Boiling point: 1860°C. Density: 2.46 g cm-3. Slightly soluble in water. Used as an insecticide; as a starting material for the synthesis of other boron compounds; as a flux for enamel and glass; mixed with 2-6% boron nitride, as a binder for boron nitride ceramic hot isostatic pressing. |DryPowder; Dry Powder, PelletsLargeCrystals; GranulesLargeCrystals|White hygroscopic powder or granules|Colorless, translucent lumps or hard, white, odorless crystals.
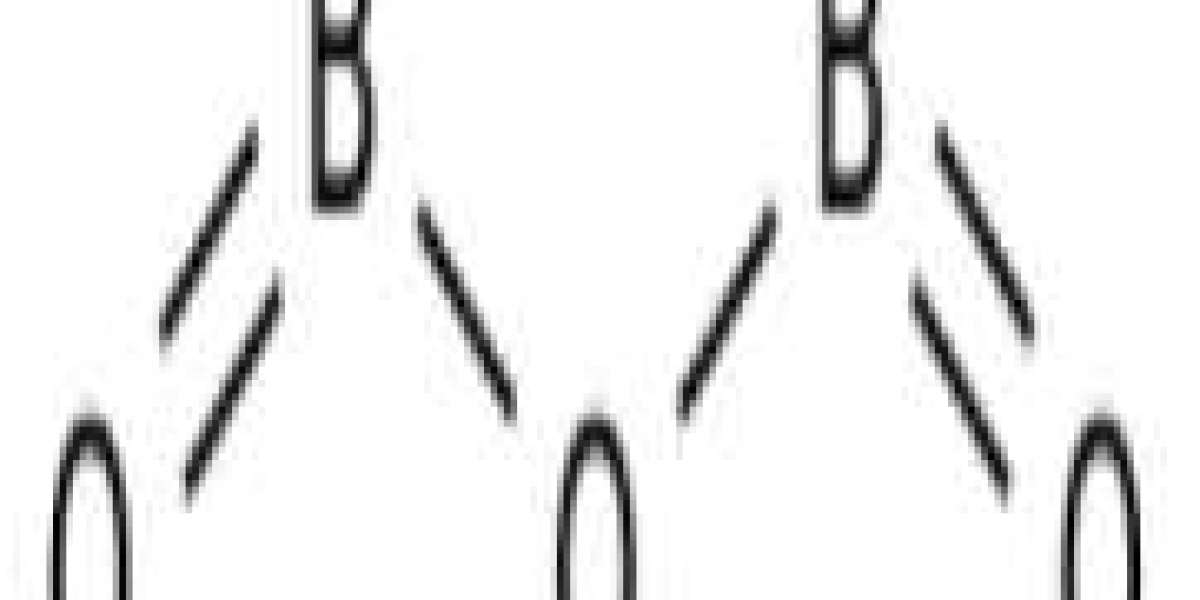
Boron oxide is colorless translucent glass block or white hard odorless crystal. Melting point 450°C; Boiling point: 1860°C. Density: 2.46 g cm-3. Slightly soluble in water. Used as an insecticide; as a starting material for the synthesis of other boron compounds; as a flux for enamel and glass; mixed with 2-6% boron nitride, as a binder for hot isostatic pressing boron nitride ceramics. |Diboron trioxide is a kind of boron oxide with molecular formula B2O3.
Boron oxide is colorless translucent glass block or white hard odorless crystal. Melting point 450 °C; bp: 1860 °C. Density: 2.46 g cm-3. Slightly soluble in water. Used as an insecticide; as a starting material for the synthesis of other boron compounds; as a flux for enamel and glass; mixed with 2-6% boron nitride, as a binder for hot isostatic pressing boron nitride ceramics.
Boron oxide is often used to replace silica in nuclear waste glass. The introduction of B breaks the Q3 unit and creates Q2, Q4 and a small amount of Q1. The presence of B has several positive effects.